What Is Digital Transformation?
The healthcare industry is in a state of disruption. Its business systems are becoming quickly outdated as society moves toward digital channels for information, transactions, and interactions.
Patients expect high-quality care that is more efficient, accessible, and equitable. These expectations compel healthcare systems to embrace data-driven digital technologies that transform current care models, business processes, and patient and member experiences.
Pushing Healthcare Provision Outward with Digital Technology
Healthcare executives must move with urgency to adopt a digital-first strategy that transforms how the healthcare industry interacts with patients and members.
A digital-first approach to healthcare (see Figure 1):
- Expands capacity and accessibility through new channels of care
- Makes possible comprehensive health and wellness initiatives in the community
- Improves quality of care, reduces costs, and increases satisfaction through digital touchpoints
- Provides personalized experiences for patients, members, and providers
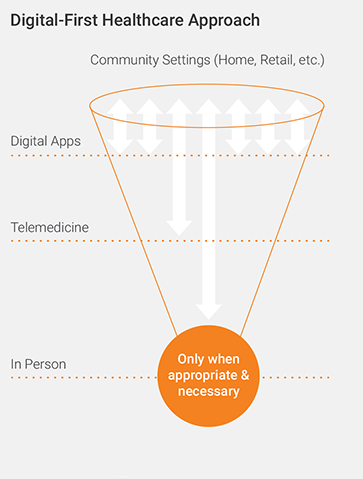
Figure 1
Four Characteristics of Healthcare Digital Transformation
The digital-first model requires healthcare to move away from a system historically organized around payment rules and siloed services. We must reimagine a new model of care and payment system.
The transformed healthcare system will exhibit four key characteristics:
- Accessible. To deliver high-quality, cost-effective, and efficient care that is available to everyone in a timely manner, the healthcare industry will have to overcome shortages in care while eliminating discrepancies in accessing quality care. This requires us to adopt new technologies for telemedicine and digital healthcare.
- Distributed. As technology empowers us to augment in-person care with remote care, healthcare providers must provide the correct care at the correct location using the best means to interact with more people. Doing so will optimize care and skilled resources, thus increasing capacity.
- Resilient. Healthcare systems must be prepared to meet surges in demand resulting from disasters and health emergencies. Resilient healthcare organizations can quickly coordinate with one another and transfer care capabilities between locations—physical and/or virtual.
- Efficient. It’s fundamental that the healthcare industry free resources to focus on the most challenging cases. This can be accomplished by automating routine and predictable tasks and moving care interactions from physical healthcare facilities to virtual or digital spaces.
Six Benefits of Healthcare Digital Transformation
A digital transformation in healthcare will increase capacity, scalability, cost-efficiency, and interoperability in the following ways:
- Driving interaction costs to zero. Digital interactions are omnichannel and without cost. Examples of digital interaction include utilizing chatbots to address questions and artificial intelligence (AI) to address complicated interactions.
- Eliminating geography as a constraint. Augmenting physical interactions with virtual care expands the time and places where patients, members, and providers can interact.
- Scaling quickly without limits. When healthcare businesses increase the number of interactions that can happen through virtual means, they can be ready to scale quickly.
- Using mass personalization to drive engagement. Because they create and consume data, digital interactions provide the opportunity to personalize patient and member interactions to the individual’s history, interests, and desired outcome.
- Enhancing accuracy and efficiency through automation. Digital processes lend themselves to automated processes that are far more consistent across channels than equivalent manual processes and can augment staff with improved, AI-guided decision making.
- Making data portable and sharable via interoperability. Digital solutions enable healthcare systems to share valuable, comprehensive data that is accurate and reliable.
Managed Data Is the Key to Digital Transformation
Healthcare data is complicated by disparate concepts and terms. It is also rife with data silos and poor data quality. These issues have made interoperability difficult and created barriers to digital transformation. The way to remove those barriers is to handle data as an enterprise asset that is inventoried, catalogued, and managed to be reliable and trustworthy. The more reliable and trustworthy data is, the better the results will be.
When you manage data as an asset, you achieve the following benefits:
- Every data element and analytic result in a report is clearly defined and commonly understood
- Your data is connected to regulations and policies that stipulate how data may be obtained, kept, used, and disposed
- There is end-to-end transparency in the lifecycle of data so that provenance can be ascertained immediately
- You can establish data sharing agreements with third parties within minutes
- You can begin using data immediately without performing lengthy profiling and quality checking
It’s impossible to keep up with the explosive growth in data by increasing manpower alone. Fortunately, data management solutions have matured. Healthcare businesses can leverage existing staff and automate data management tasks by employing AI and ML to solve problems and complete complex data management activities that used to be impossible at an enterprise scale.
How Healthcare Executives Use Data Management
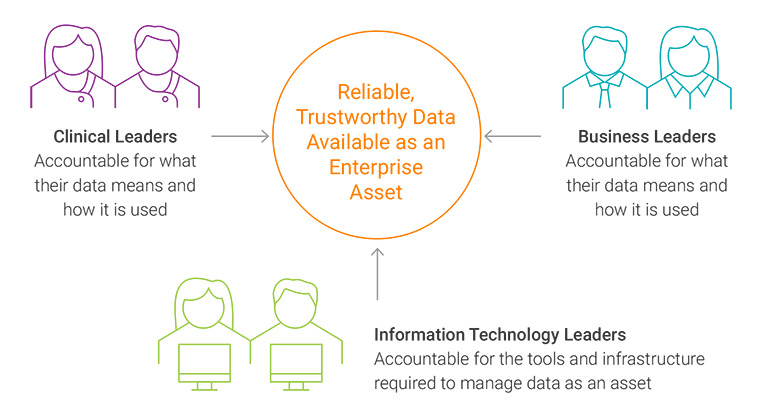
Figure 2
Data management is a core business function, not a technology endeavor. It cannot be consigned to IT where the tools, technology, and implementation are detached from clinical and business requirements. This requires a collaborative data management team structure that nonetheless retains clear areas of responsibility (see Figure 2).
When data management is done correctly, clinical and business users are the authorities over what their data means and how it is used; IT is accountable for the data management tools, data management infrastructure, and data management training.
Successful Healthcare Digital Transformation Needs Cloud
Healthcare organizations are moving applications and data workloads to the cloud because the business and clinical benefits are clear. Doing so empowers the healthcare industry to:
- Increase business agility. It takes only minutes to stand up new applications and data workloads with a cloud provider, in comparison to the months it can take in an on-premises data center.
- Deliver performance and scale. In the cloud environment, healthcare businesses can perform tasks more quickly and scale the scope of a task or scale the number of users performing a task. Users can scale processing and storage capacity up or down as needed.
- Improve IT innovation. Cloud service providers continually update their services in the background, eliminating the need for healthcare companies to keep pace with new technologies and enabling healthcare staff to continue working. Cloud environments also enable healthcare businesses to experiment quickly for low cost and with low risk, promoting innovative solutions to business and clinical problems.
- Avoid technical staffing and retention challenges. Non-technical team members can easily access and use cloud-based services to support business and clinical analytics and processes. The most labor-intensive IT processes are automated, minimizing the need to recruit staff for tough-to-fill technical roles.
- Strategize in a multicloud world. There are multiple cloud service providers for the healthcare industry to choose from. Each vendor has different strengths, making it probable that healthcare services will operate in a multicloud environment.
How to Leverage Data Governance to Achieve Digital Transformation in Healthcare
The foundation of healthcare’s digital future is reliable and trustworthy data. The way you achieve reliable and trustworthy data is to govern it. Data governance ensures healthcare organizations support privacy rules, security, and complex regulations from end to end and meet evolving compliance requirements.
Data governance provides the ability to:
- Know where all your data assets reside, where the data goes, how it’s been transformed, who consumes it, and for what purpose
- Have a common understanding of what data means, who the data owners are, which quality rules and KPIs are relevant to the data, and who decides if data is correct and fit for use
- Align data ownership, data consumers, and allowable uses to industry regulations and enterprise data policies in such a way that compliance is audited continuously
- Ensure that data is used and shared in a secure and compliant manner and with patient consent
Healthcare Digital Transformation in Practice
Informatica empowers healthcare organizations to succeed in their digital transformation journeys.
Cloud application integration: Providing faster patient diagnoses
A genetics research company needed to integrate enterprise data sources with complex workflows to expedite test results for faster patient diagnosis. To solve this issue, the company utilized Informatica Intelligent Cloud Services and Informatica Cloud Application Integration to orchestrate data flows between enterprise applications and a data warehouse. This minimized the time required to get results back to a physician.
Cloud analytics: Enabling more effective healthcare
Franciscan Alliance is a rapidly growing healthcare system in northern and central Indiana, as well as in eastern Illinois. In a drive to deliver high-quality care, Franciscan leveraged Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics and Informatica’s Enterprise Data Catalog and Intelligent Cloud Services. The organization built a complex analytics framework integrating paid claims with current patient encounters to point out potential areas of concern. The solution also helped the organization meet the demands of emerging situations, such as COVID-19 and CARES Act reporting requirements, in days rather than weeks or months.
Data governance: Delivering a timely, coordinated response
UNC Health, a statewide nonprofit healthcare system, needed to enhance data governance and enable self-service analytics for executives and business users. To solve this issue, the healthcare system integrated Informatica Data Catalog with Axon Data Governance to make cataloged data available and provide a collaborative shared view of data assets. This enables data analysts, developers, and architects to quickly find and understand data and expedite analysis, providing clear and accurate information to facilitate decision making.
Six Key Steps to Achieving Healthcare Digital Transformation
Healthcare systems embarking on the digital transformation journey will make quick progress by following six steps:
- Implement a buddy system. Pair business and IT leaders to jointly drive the delivery of the required outcomes through collaboration, communication, and prioritization.
- Create clear roles, responsibilities, and accountabilities.Use a project management framework to define and communicate stakeholder roles across the organization.
- Commit to cloud first, then get to work. Choose your primary cloud ecosystem and implementation partners, then define your enterprise cloud data architecture and understand all the competencies required to manage it.
- Choose where AI and machine learning (ML) can have the greatest transformative impact in your healthcare business and plan around that.
- Focus on delivering tangible clinical or business value—fast. Don’t allow your digital transformation journey to devolve into technical or architectural milestones that sidetrack the goal of delivering true value.
- Govern just enough data to get to value fast. Start a project, earn credibility, and deliver results quickly to build momentum for the next phase of your digital transformation.
Meet the Intelligent Data Management Cloud
The Informatica Intelligent Data Cloud is the healthcare industry’s most complete and modular enterprise data solution. The AI-driven platform ensures data is trusted, protected, governed, accessible, timely, relevant, and actionable—enabling healthcare organizations to deliver faster and better data-driven digital transformation outcomes.